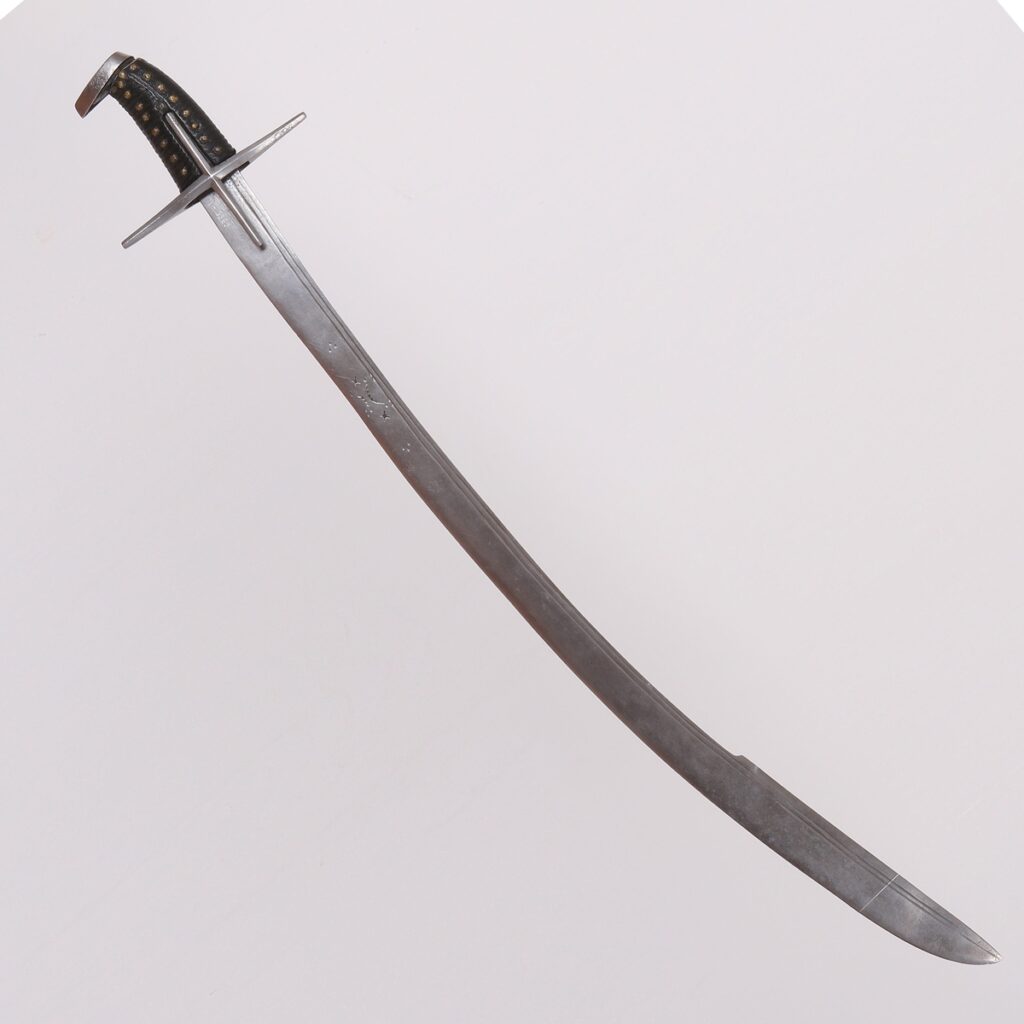

07 Sabre, Hungary, 2nd half of 17th century
Fotogalerie




The sabre came to Europe from the East and became more popular during the Turkish wars when the nations fighting the Turks, the Hungarians, Russians and Poles, became familiar with it. The Turkish raids in the 16th century made the Turkish kilij sabre, which became widespread especially in the 17th century. The dominant influence of the kilij lasted until the end of the 18th century, when Napoleonic armies brought a Persian sabre called the shamshir from Egypt. The shamshir has a blade tapering towards the tip while the kilij has a yelman, a blade widened in the lower third and fitted with a second (false) blade.
This Hungarian sabre is inspired by the shape of a Turkish kilij. Its single-edged blade is slightly curved and has two narrow grooves on both sides. The wooden grip is covered with leather and reinforced with brass rivets in the shape of rosettes. The iron fittings of the hilt consist of a wide cross-guard and a boat-shaped pommel.
In Europe, the sabre became widely used as soon as individual armies began to introduce regular corps of light hussars. The characteristics of this weapon, its lighter weight and considerable effectiveness, suited the mission of the light cavalry, which was to be highly mobile and fought in a similar way as the Turkish and Tartar armies on the vast steppes.
Length 850 mm, blade length 745 mm, blade width 38 mm, weight 798 g.
Aktuálně

Připomínáme si 176 let od narození prezidenta T. G. Masaryka

Připomínáme si výročí bitvy u Sokolova - 8. 3. 1943

Připomínka data narození: parašutista Jan Hrubý / 4. 3. 1915 - 18. 6. 1942
Připomínka 20. výročí ukončení humanitární operace NATO Winter Race v Pákistánu, v níž byli zapojeni i čeští odborníci a vojáci









